Shoulder Arthritis
A degenerative shoulder joint condition leading to pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility
Shoulder arthritis is a degenerative condition that results in pain, stiffness, and restricted movement in the shoulder. The shoulder is a highly complex joint, allowing a wide range of motion. It consists of two main joints: the glenohumeral joint, where the arm bone meets the shoulder socket, and the acromioclavicular joint, where the collarbone connects to the shoulder blade. Arthritis can affect either or both of these joints, causing a significant impact on everyday activities.
Several types of arthritis can affect the shoulder, with osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and post-traumatic arthritis being the most common. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and available treatment options helps individuals manage the condition effectively, improving quality of life.
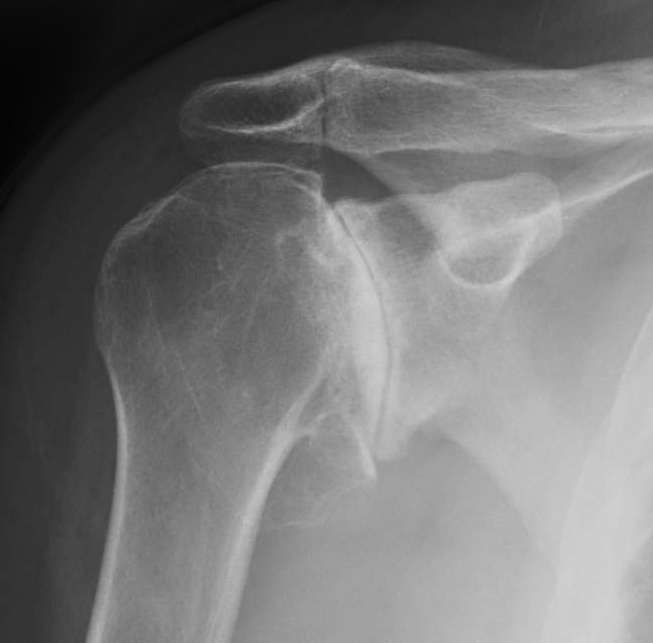
Types of Shoulder Arthritis
Melbourne Orthopaedic Clinic treat a variety of shoulder arthritis types, including:
- Osteoarthritis: Often referred to as “wear-and-tear” arthritis, this form occurs as the cartilage in the shoulder joint breaks down over time, causing pain and stiffness.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA): An autoimmune condition where the immune system attacks healthy joint tissues, leading to inflammation and eventual joint damage. RA often affects both shoulders symmetrically.
- Post-Traumatic Arthritis: This type of arthritis develops after a previous shoulder injury such as a fracture or dislocation. The damage caused by the injury can lead to cartilage degeneration over time.
- Rotator Cuff Tear Arthropathy: This occurs following a long-standing, untreated rotator cuff tear, which compromises joint stability and eventually leads to cartilage damage and arthritis.
Symptoms of Shoulder Arthritis
Common symptoms of shoulder arthritis include:
- Pain: Gradual onset of shoulder pain that worsens with movement or over time, especially during physical activities.
- Stiffness: A reduced range of motion that makes it difficult to perform everyday tasks such as reaching overhead or behind your back.
- Swelling and Tenderness: The shoulder may appear swollen, and the joint might be tender when touched.
- Grinding or Clicking Sensation: As the cartilage wears down, the bones may rub against each other, causing a grinding or clicking sound during movement.
- Weakness: Muscle weakness around the shoulder joint can occur, making it difficult to lift objects or carry out normal daily activities.
Diagnosis of Shoulder Arthritis
Diagnosing shoulder arthritis begins with a comprehensive physical examination, combined with advanced imaging and diagnostic tests. Your surgeon will assess your shoulder’s range of motion, strength, and any tenderness around the joint. Other diagnostic measures include:
- X-rays: To assess cartilage loss, joint space narrowing, and bone spurs.
- MRI or CT scans: These detailed scans help evaluate the soft tissues, including the cartilage and tendons, and are particularly useful for more complex cases.
- Blood tests: If rheumatoid arthritis or other autoimmune conditions are suspected, blood tests are conducted to check for inflammation markers and specific antibodies.
Treatment Options for Shoulder Arthritis
Our treatment plan for shoulder arthritis is tailored to the type and severity of the condition. Our first line of treatment includes non-surgical options to manage pain and improve mobility, such as:
- Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers such as paracetamol or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to reduce pain and inflammation.
- Physiotherapy: A tailored physiotherapy program can help strengthen the muscles around the shoulder and improve flexibility.
- Activity Modification: Adjusting or avoiding activities that put excessive strain on your shoulder, such as lifting heavy objects or repetitive overhead movements, can help manage symptoms. Low-impact exercises like swimming and walking are recommended to maintain joint mobility.
- Corticosteroid Injections: These injections provide temporary relief by reducing inflammation in the joint.
- Heat and Cold Therapy: Applying heat to relax shoulder muscles or cold packs to reduce swelling and numb pain can help alleviate discomfort.
If these conservative treatments are not effective, surgical options may be considered:
- Arthroscopic Surgery: A minimally invasive procedure where damaged cartilage or bone spurs are removed from the joint to improve mobility and reduce pain.
- Shoulder Replacement Surgery: For severe cases of arthritis, partial or total shoulder replacement surgery may be recommended to replace the damaged joint with an artificial one.
Managing Shoulder Arthritis: Lifestyle and Home Care
In addition to medical treatments, lifestyle changes and home care strategies play a vital role in managing shoulder arthritis. We encourage our patients to focus on:
- Staying Active: Engage in gentle exercises that maintain joint flexibility and strength without overloading the shoulder, such as swimming or yoga.
- Healthy Diet: Maintain a balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods like fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids, which may help reduce inflammation.
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight reduces the stress on your joints and can help alleviate some of the symptoms associated with arthritis.
Our goal is to provide comprehensive care and a range of treatment options for shoulder arthritis to help you live a more active and pain-free life. Early diagnosis and the right treatment can significantly improve your shoulder function and overall quality of life. Whether you’re exploring non-surgical treatments or considering surgery, we are here to guide you every step of the way.

