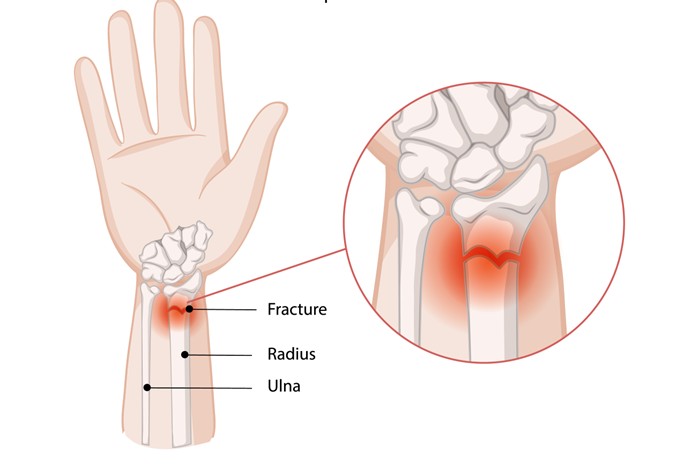
Hand and Wrist Fractures
A condition characterised by a break or crack in the bones of the hand or wrist
The bones of the hand and wrist are essential for strength, stability, and fine movement. Fractures in this region are common and can occur from falls, sporting injuries, workplace accidents, or direct trauma. These injuries range from simple, stable breaks that heal with splinting to more complex fractures involving multiple bones and joints.
Symptoms often include pain, swelling, bruising, deformity, and difficulty moving the hand or wrist. Because the bones are closely linked with tendons, ligaments, nerves, and blood vessels, even a small fracture can significantly affect hand function if not treated properly.
Prompt diagnosis and appropriate management are important to restore alignment, support healing, and prevent long-term stiffness or loss of movement.
Causes of Hand and Wrist Fractures
Hand and wrist fractures can occur due to various causes, including:
- Falls: Falling onto an outstretched hand is a common cause of fractures in the wrist or hand bones, particularly in active individuals or the elderly.
- Direct Impact: A direct blow to the hand or wrist, often seen in contact sports or accidents, can lead to fractures.
- Overuse and Stress: Repeated stress or pressure on the wrist bones can lead to small fractures, particularly in athletes who engage in weight-bearing or high-impact sports.
- Weak Bone Structure: Conditions such as osteoporosis or bone density loss can increase susceptibility to fractures, even with minimal impact.
Symptoms of Hand and Wrist Fractures
The symptoms of a hand or wrist fracture may vary depending on the location and severity of the break but can include:
- Severe Pain: Pain is often immediate and sharp, particularly when attempting to move or put weight on the affected area.
- Swelling and Bruising: Swelling, bruising, or tenderness around the fracture site is common following a break.
- Deformity or Misalignment: In cases of more severe fractures, the hand or wrist may appear visibly misaligned or deformed.
- Limited Range of Motion: Difficulty moving the hand or wrist, especially with fractures near joints, can occur.
- Numbness or Tingling: Nerve irritation or injury near the fracture site may cause tingling or numbness in the fingers or hand.
Diagnosis of Hand and Wrist Fractures
A prompt and accurate diagnosis is important to ensure proper healing and to reduce the risk of long-term stiffness or loss of function. Assessment usually combines a detailed history, physical examination, and imaging tests.
- Medical history
- Prof Sallen will ask how the injury occurred, when symptoms began, and whether there was any immediate swelling, bruising, or deformity.
- Information about your work, hobbies, and hand use helps determine how the injury affects your daily activities.
- Physical examination
- The hand and wrist are carefully assessed for swelling, tenderness, bruising, or abnormal alignment.
- Movement of the fingers, grip strength, and wrist stability are checked.
- Circulation and nerve function are also tested, as injuries may affect blood vessels or nerves in the area.
- Imaging tests
- X-rays are the most common investigation and can confirm the presence, type, and location of a fracture.
- CT scans may be recommended for complex or joint-related fractures to provide more detailed information.
- MRI scans can sometimes be used if soft tissue damage (such as ligament or cartilage injury) is suspected alongside the fracture.
- Differential diagnosis
- Not all wrist or hand pain after an injury is due to a fracture. Sprains, ligament injuries, and tendon damage may produce similar symptoms, so careful assessment is required.
With this information, Prof Sallen can confirm whether a fracture is present, determine its severity, and recommend the most suitable treatment plan for recovery.
Treatment Options for Hand and Wrist Fracture
Treatment for hand and wrist fractures focuses on realigning the bones, promoting healing, and restoring function. Prof. Sallen offers a variety of treatment options tailored to the nature of the fracture and your specific needs.
Non-Surgical Treatments
Many fractures can be treated with non-surgical methods, including:
- Casting and Splinting: Immobilising the affected area with a cast or splint helps to align the bones and support healing while limiting movement.
- Pain Management: Over-the-counter pain medications or prescription analgesics may be recommended to manage pain associated with the fracture.
- Physiotherapy: After initial healing, a tailored rehabilitation program may be provided to restore mobility, strength, and flexibility to the affected area.
Surgical Treatments
For more severe fractures, surgical intervention may be necessary to ensure proper alignment and healing. Surgical options include:
- Open Reduction and Internal Fixation (ORIF): This procedure involves realigning the bone fragments and securing them with screws, plates, or pins to maintain stability during healing.
- External Fixation: In cases where internal fixation is not possible, an external frame may be used to stabilise the bones while they heal.
- Bone Grafting: For fractures involving significant bone loss or complex injury, a bone graft may be used to support healing and restore bone structure.
At Melbourne Orthopaedic Clinic, our dedicated team is committed to providing comprehensive care for hand and wrist fractures. We work closely with each patient to develop a personalised treatment plan aimed at reducing pain, promoting healing, and enhancing functional recovery, helping patients regain confidence and return to their everyday activities.