Gluteal Tendinopathy
Degeneration of the gluteal tendons causing pain, weakness, and reduced mobility
Gluteal tendinopathy is a condition characterised by the degeneration of the gluteal tendons, typically located on the outside of the hip. This condition leads to pain, weakness, and discomfort, particularly during activities like walking, climbing stairs, or standing from a seated position. Melbourne Orthopaedic Clinic focuses on diagnosing and treating gluteal tendinopathy to help alleviate pain and restore normal function.
On this page, you’ll learn about:
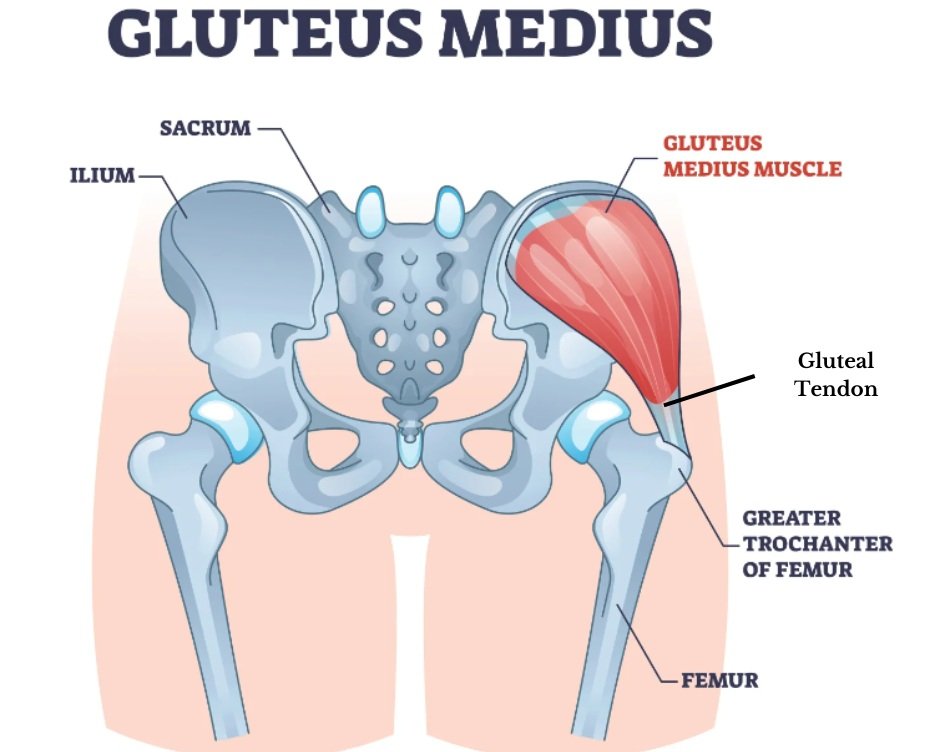
Causes Of Gluteal Tendinopathy
Gluteal tendinopathy often arises due to overuse or repetitive stress on the gluteal tendons, but several other factors can contribute to its development. Common causes include:
- Repetitive Overuse: Activities that involve repetitive hip movements, such as running, cycling, or squatting, can lead to microtrauma of the gluteal tendons over time.
- Hip Muscle Weakness: Weakness in the gluteal muscles can increase strain on the tendons, leading to inflammation and degeneration.
- Injury or Trauma: Acute injuries, such as a fall or direct impact to the hip area, can cause damage to the tendons, resulting in tendinopathy.
- Leg Length Discrepancy: Having one leg shorter than the other can lead to altered gait mechanics and uneven stress on the hip and tendons.
- Structural Issues: Abnormalities in hip structure, such as hip dysplasia or osteoarthritis, can contribute to increased stress on the gluteal tendons.
Symptoms Of Gluteal Tendinopathy
Symptoms of gluteal tendinopathy can develop gradually and worsen over time. Common symptoms include:
- Hip Pain: Pain is typically felt on the outer side of the hip and may radiate down the thigh. It often worsens with activities that involve hip movement, such as walking, climbing stairs, or getting in and out of a car.
- Tenderness: The area over the affected gluteal tendons may be tender to touch, and pressing on the site can provoke pain.
- Weakness: Individuals may experience weakness in the hip, particularly when attempting to perform activities that require hip stabilisation, such as balancing on one leg.
- Stiffness: Affected individuals may notice stiffness in the hip, especially after prolonged sitting or inactivity.
- Difficulty with Daily Activities: Pain and weakness can limit the ability to perform everyday activities, impacting mobility and quality of life.
Diagnosis Of Gluteal Tendinopathy
At Melbourne Orthopaedic Clinic, a thorough assessment is performed to diagnose gluteal tendinopathy, which may include:
- Physical Examination: Your doctor will conduct a comprehensive examination of the hip, assessing your range of motion, strength, and areas of tenderness. Specific movements may be tested to elicit symptoms associated with gluteal tendinopathy.
- Imaging Tests: Imaging techniques such as X-rays or MRI may be used to confirm the diagnosis and assess the extent of tendon degeneration or inflammation, ruling out other conditions that may mimic the symptoms.
Gluteal Tendinopathy Treatment Options
Treatment for gluteal tendinopathy aims to relieve pain, improve strength, and restore mobility. At Melbourne Orthopaedic Clinic, we offer both non-surgical and surgical options tailored to individual needs.
NON-SURGICAL TREATMENTS
Most cases of gluteal tendinopathy respond well to non-surgical treatments, including:
- Physiotherapy: A physiotherapist will guide you through targeted exercises designed to strengthen the gluteal muscles, improve flexibility, and enhance hip stability, which can help alleviate symptoms.
- Medications: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can be recommended to reduce pain and inflammation associated with gluteal tendinopathy.
- Activity Modification: Avoiding activities that exacerbate symptoms, such as prolonged standing or high-impact exercises, can reduce strain on the gluteal tendons.
- Injections: Corticosteroid or platelet-rich plasma (PRP) injections may be considered to provide relief from pain and inflammation, especially for persistent cases.
SURGICAL TREATMENTS
If non-surgical treatments are ineffective or the condition severely affects your quality of life, surgical intervention may be explored. Surgical options can include:
- Tendon Repair or Debridement: In cases of significant tendon degeneration, a surgical procedure may be performed to repair the damaged tendon or remove degenerated tissue, promoting healing and restoring function.
At Melbourne Orthopaedic Clinic, we understand the impact of gluteal tendinopathy on your daily life and physical activity. Our team is dedicated to providing personalised care and effective treatment options to help you regain mobility and reduce pain. Whether through physiotherapy, lifestyle modifications, or surgical interventions, we work collaboratively with you to achieve the best possible outcomes and support your journey towards recovery